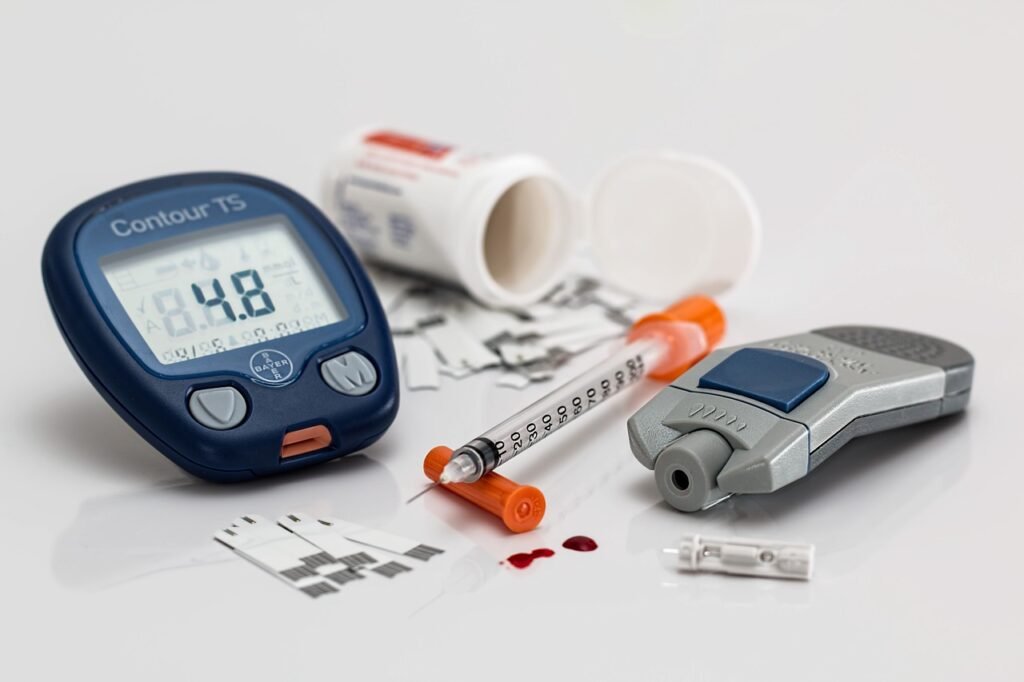
For individuals living with diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. In this article, we will explore the significance of regular glucose monitoring and the role of the HbA1c test in diabetes care. This article aims to provide insight into the importance of understanding these measurements, empowering individuals with diabetes to take control of their health. By grasping the nuances of glucose levels and HbA1c, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize their diabetes management and overall well-being.
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for individuals with diabetes as it provides real-time data on how their bodies are responding to dietary choices, medication, and lifestyle. Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) allows individuals to track fluctuations in glucose levels throughout the day and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. This data can help identify patterns, such as post-meal spikes or nighttime lows, enabling more precise management.
The HbA1c test, on the other hand, offers a broader view of glucose control over the past two to three months. It measures the average percentage of hemoglobin in the blood that is bound to glucose, reflecting long-term blood sugar levels. This test provides valuable insights into overall glycemic control and can help individuals and healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of the diabetes management plan. The target HbA1c level varies based on individual circumstances, but it generally serves as a benchmark for diabetes management goals.
Monitoring blood glucose levels and understanding the HbA1c test are integral components of effective diabetes management. Regular monitoring allows individuals to make timely adjustments to their treatment plan, promoting better short-term glucose control. Meanwhile, the HbA1c test offers a comprehensive perspective on long-term glycemic control, guiding healthcare providers and individuals in assessing the effectiveness of their management strategies. By embracing both of these tools and working closely with their healthcare team, individuals with diabetes can proactively manage their condition, reduce the risk of complications, and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.